|
Camera Specifics
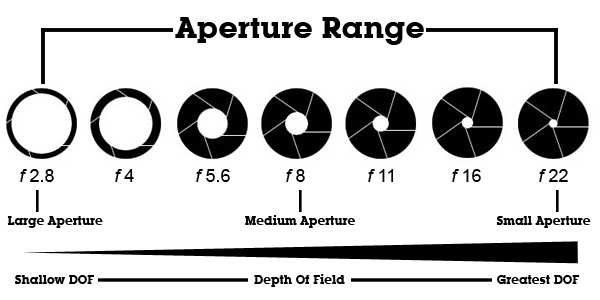
Aperture Size - Deals with the amount of light let in. Acts a lot like our retinas.
Shutter Speed - Deals with the amount of time the light of an image is exposed to the Recording medium.
ISO - Deals with how sensitive the sensor is
Resolution - Deals with the number of pixels each axis of an image
|
|
Auto Focus
Auto focus has made taking a picture much easier. The old way of twisting a lens is not needed anymore (unless you have a professional camera). For the basic camera that a consumer can buy at the store or the camera that is on all our smart phones, auto focus is included.
There are three methods that can be used for auto focus.
Auto focus is a great and useful tool.but can be a pain at times. At times it may be focusing on an object that you may not want it to. it may focus on the closer object although you intended for it to focus on a object that was further away.
There are three methods that can be used for auto focus.
- Sonar - usage of sound to determine the distance of what object is in the camera view.
- IR lasers - using the infrared lasers to determine the distance and focus needed on the object.
- Image contrast - measuring contrast within sensor field, does not involve distance but uses the light of object to determine focus
Auto focus is a great and useful tool.but can be a pain at times. At times it may be focusing on an object that you may not want it to. it may focus on the closer object although you intended for it to focus on a object that was further away.
EXIF (Exchangeable File Format)
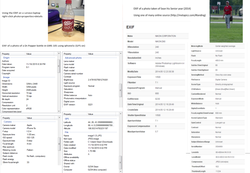
Most digital cameras save images as JPEG files, along with the photo there is much more information that is saved,automatically information is stored along with the photo.
(Excangeable Image Format (EXIF))
There is information about the camera and photo included in the file.
The information is saved so it is easier to tell what was going on throughout the shot.
For example, it allows you to view the settings that were used even if they were not manually set.
3 ways EXIF can be used:
GPS LOCATION
As many people may know, location settings on cameras and especially phones can be used for many things.
(Excangeable Image Format (EXIF))
There is information about the camera and photo included in the file.
The information is saved so it is easier to tell what was going on throughout the shot.
For example, it allows you to view the settings that were used even if they were not manually set.
3 ways EXIF can be used:
- If you are into photography you can see what someone else’s settings were like when their shot was taken. (Flickr.com)
- You can see what settings you used for the shot without manually recording what was done.
- if something is wrong with your camera than it is easier to see where it went wrong using the EXIF information.
GPS LOCATION
As many people may know, location settings on cameras and especially phones can be used for many things.
- Using location on a phone or camera can be DANGEROUS
- When a photo is posted on social media (Facebook) the EXIF is wiped out.
- There is possibility that someone may be able to see your location if the location settings are on.